Comparing values for equality is a common functionality when dealing with worksheets. In this tutorial we're going to review the basic usage of VBA Excel not equal.
This is an operator in VBA which is also called the negation operator. The operator looks like this (). If the two values are not equal it will return true, and if the two values are not equal it will return false. We get the exact opposite answer from the equal sign (=).
With the equality operator '=' if we have 25 = 25 it will return true.
However, for Not Equal, for example, 25 25, this will return false.
Code:
Sub example1()
Dim i As String
i = 25 <> 25
MsgBox i
End Sub
In the above code, we are trying to check if 25 is not equal to 25.
Let's see the result on our message box below:
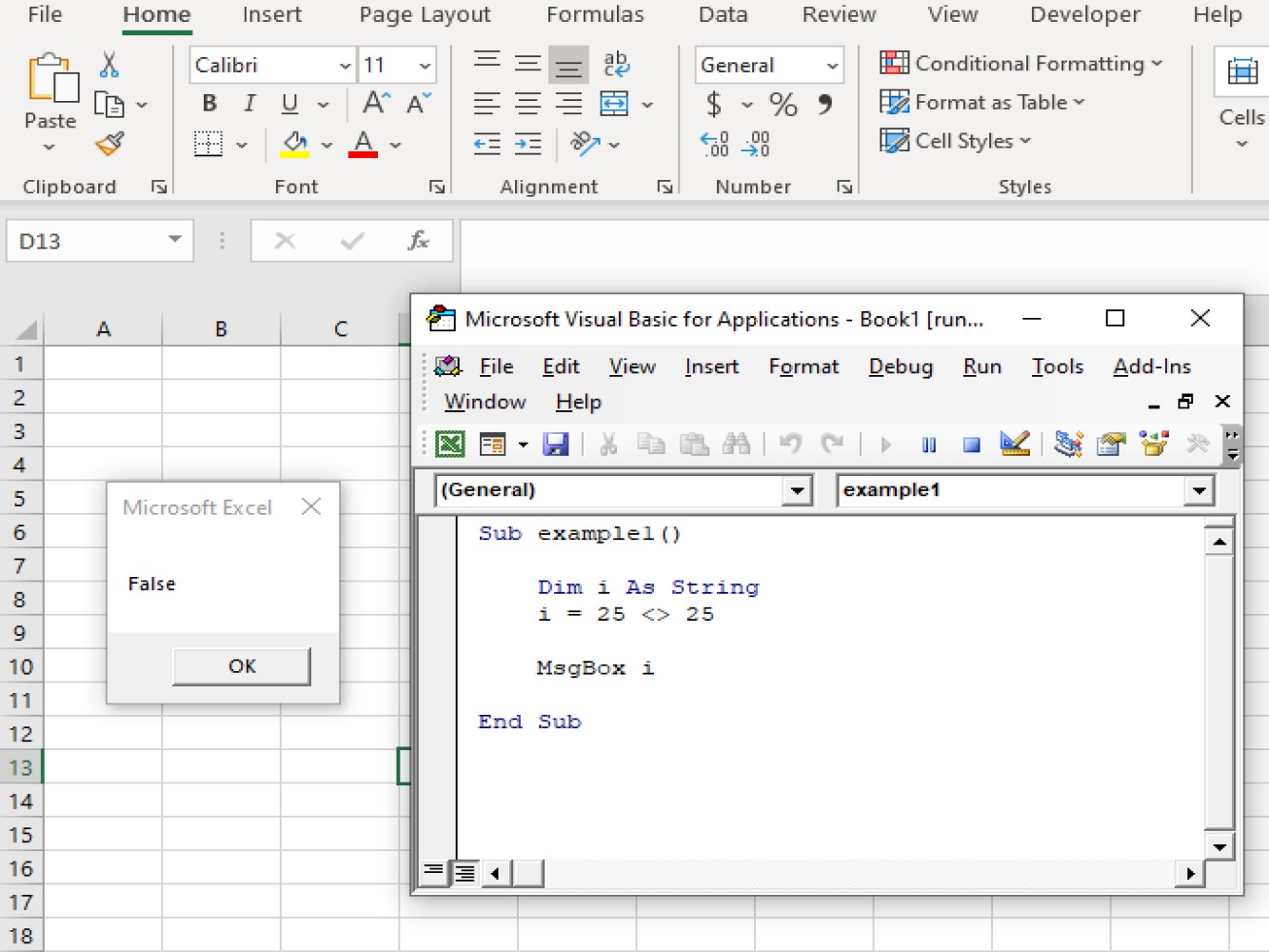
We False as the result because 25 is not equal to 25.
Let's change the comparison:
Code:
Sub example2()
Dim i As String
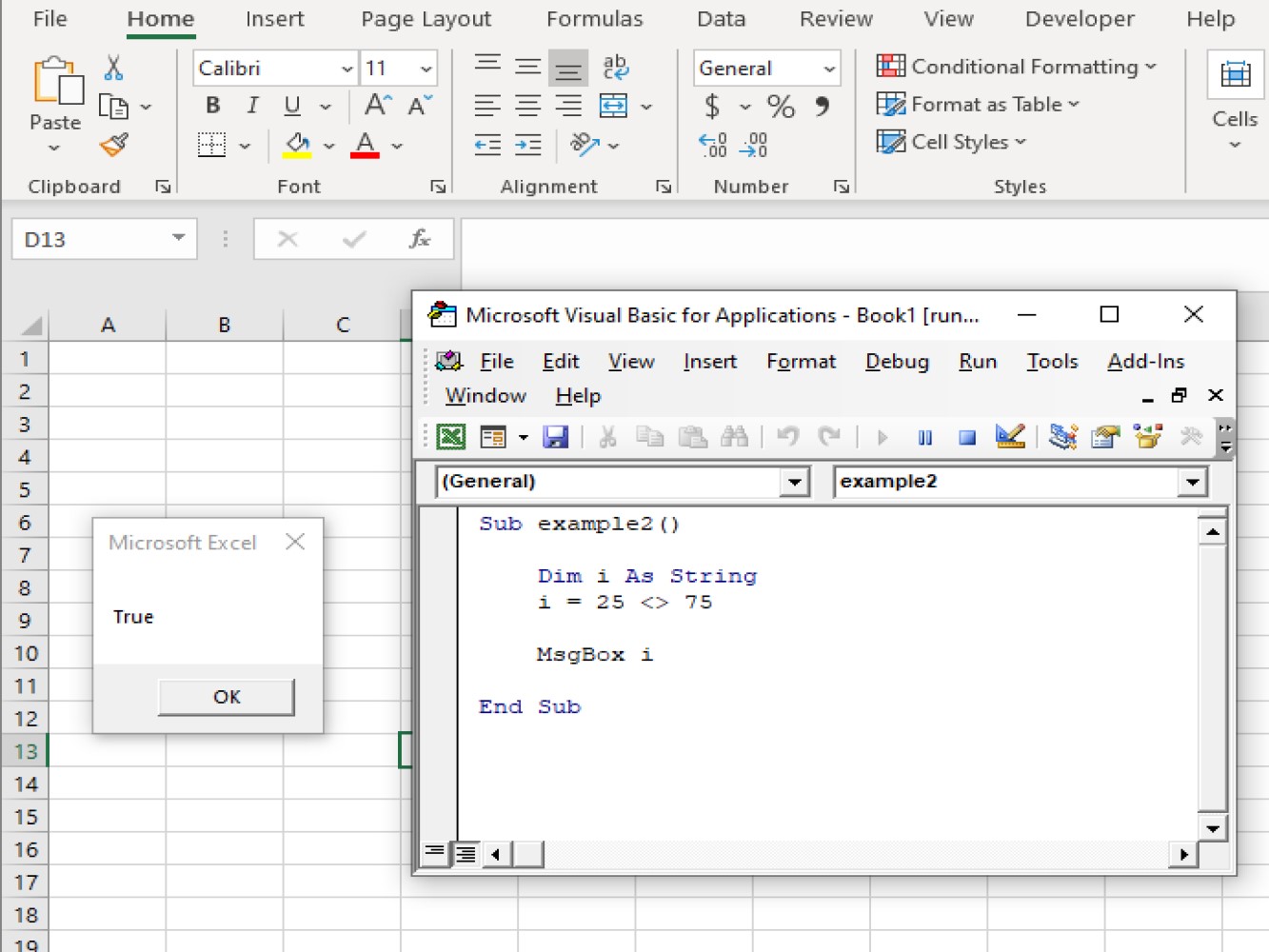
i = 25 <> 75
MsgBox i
End Sub
The above code gives us True on the message box because 25 is not equal to 75.
Code:
Sub example3()
Dim i As Integer
For i = 2 To 9
If Cells(i, 1) <> Cells(i, 2) Then
Cells(i, 3).Value = "Different"
Else
Cells(i, 3).Value = "Same"
End If
Next i
End Sub
Code explanation:
Dim i As Integer - in this part, we have set our integer as i.For i = 2 To 9 - this refers to the cell range that we are working on.If Cells(i, 1) Cells(i, 2) Then - this will indicate VBA that we are using the if method. And we are using the syntax for equal or not equal to.Cells(i, 3).Value = "Different"
Else
Cells(i, 3).Value = "Same"
End If - this defines as the cell range we work on and the values to be written on column 3 if the values are different or same.And now, see the result below:
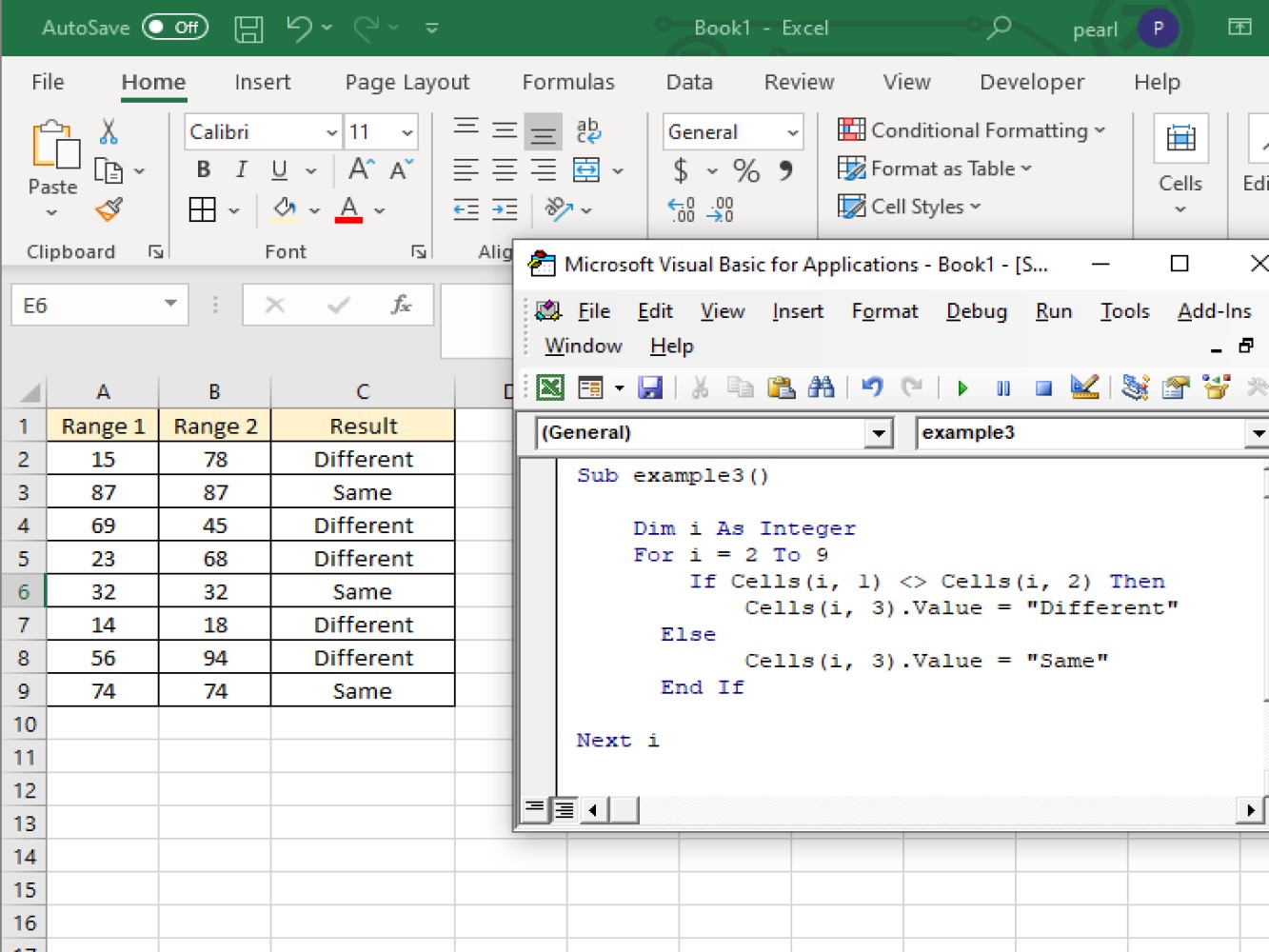
As per the result, you can see in column C, it states whether the number on the two ranges are the same or not.
Below is a sample of an active workbook with three different worksheets opened.
See the below code that can hide the unnecessary worksheets and leave the one we wished to work on.
Code:
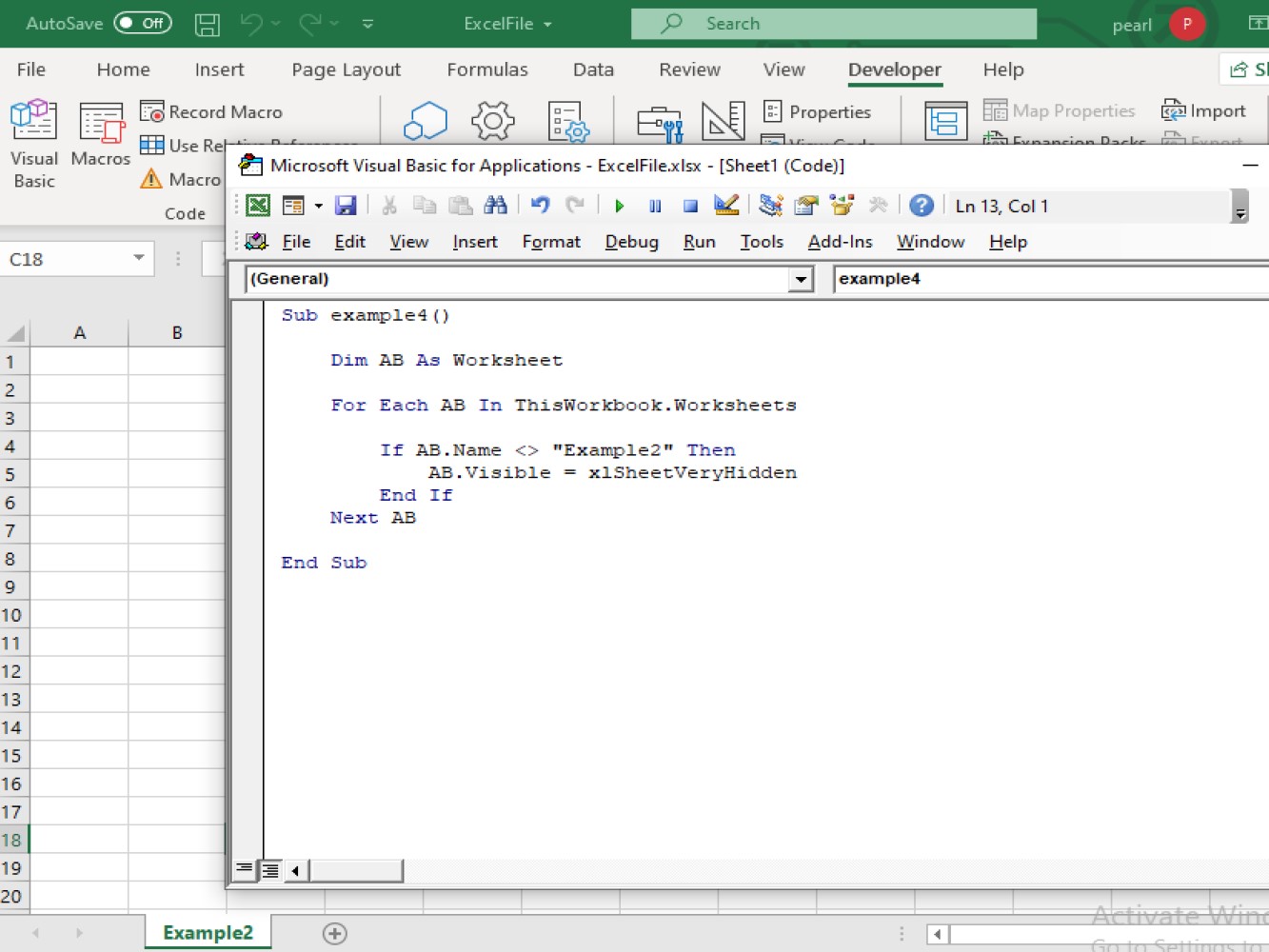
Sub example4()
Dim AB As Worksheet
For Each AB In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If AB.Name <> "Example2" Then
AB.Visible = xlSheetVeryHidden
End If
Next AB
End Sub
Code explanation:
Dim AB As Worksheet - we have set AB as our workbook's integer.For Each AB In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets - this defines as that we need to work on this workbook and the worksheets.If AB.Name "Example2" Then
AB.Visible = xlSheetVeryHidden
End If - this will instruct VBA to hide the worksheets except Example2. And this also refers that we are using the if method.And the result will be:
Code:
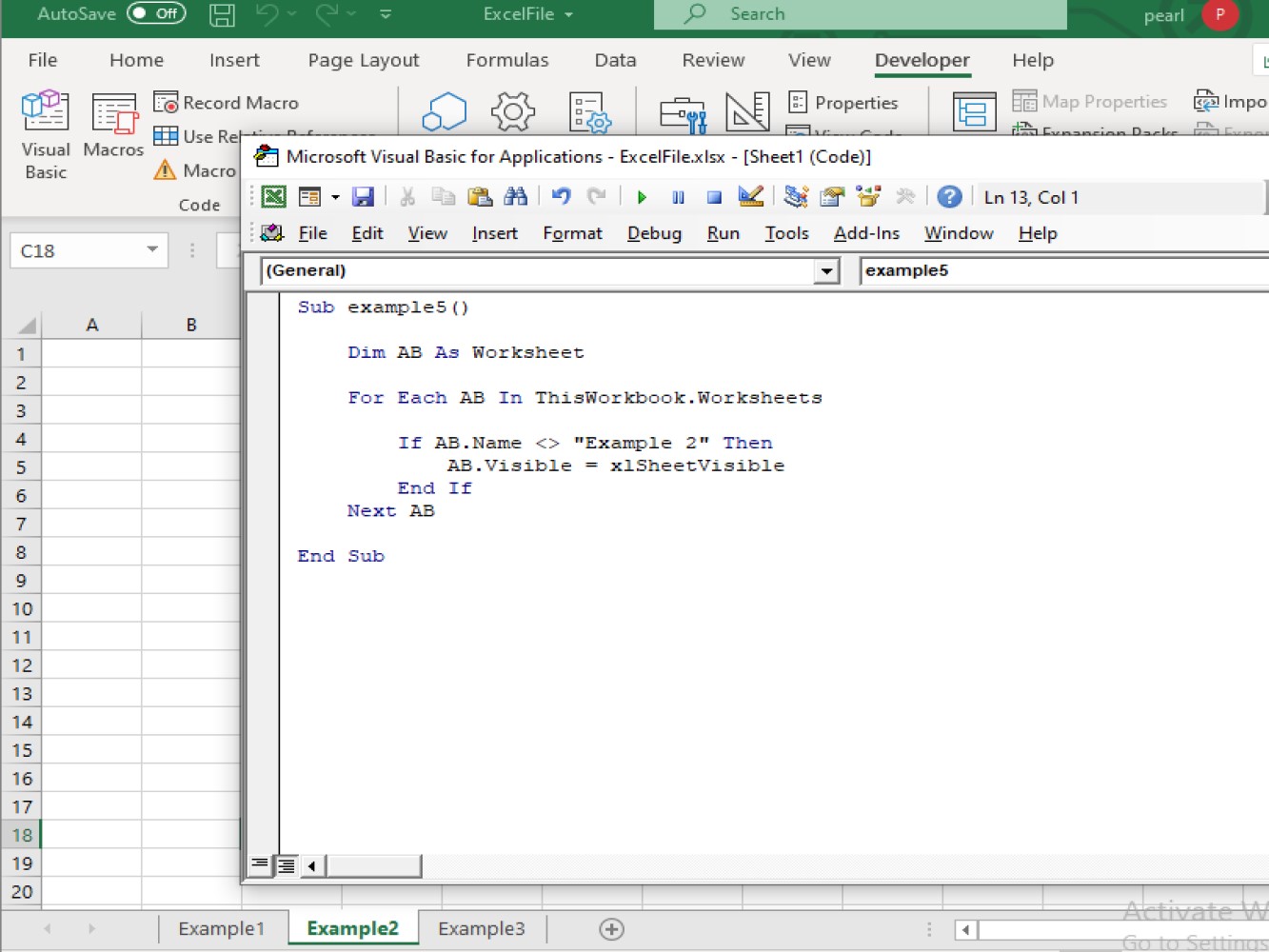
Sub example5()
Dim AB As Worksheet
For Each AB In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If AB.Name <> "Example 2" Then
AB.Visible = xlSheetVisible
End If
Next AB
End Sub
The above code will unhide and show all the hidden worksheets on the workbook.
See below result:
The Not Equals operator can be a little confusing at first but it's easy to think about as the opposite of the equality operator. We showed a couple examples of using it including one where we unhid all the worksheets who's name was not equal to "Example 2". There are tons of use cases for this operator so it's a great tool to have in your toolbelt.